Corporate Development and External Innovation Through M&A and Corporate Venturing – Part 2: Critical Success Factors
June 13, 2019Bitkom Membership
July 29, 2019Market Developments
Large companies nowadays have to deal with numerous challenges. The shortage of skilled workers is an omnipresent issue, as well as the emergence of disruptive technologies and new and agile competitors. In 1958, the average lifespan of a company was 61 years, but today it is heading towards an average of 18 years. On the other hand, companies often lack of innovations in the business fields of the future, as well as sufficient preparation for the digitalization of the value chain. [1]Many companies are responding to the growing threat of disruptive technologies by increasing investments in R&D. It can be observed that R&D expenses have risen steadily since the 1990s. However, it is also the case that companies are still making slow and cumbersome progress. [6]
The strategic corporate development department is currently confronted with this situation. Its importance is being increased by the latest developments. One of its major tasks is the identification and generation of innovations. This can be done by the following measures:
- Acquisition of other companies (M&A activities)
- Establishment of intrapreneurship programs for internal innovation development
- Use of scouts to search for startups
- Development of partnerships with startups
- Setting up incubator or accelerator programs
- Implementation of corporate venture capital units (CVC units)
- Establishment of intrapreneurship programs for internal innovation development
- Use of scouts to search for startups
- Development of partnerships with startups
- Setting up incubator or accelerator programs
- Implementation of corporate venture capital units (CVC units)
Although companies are increasingly using these measures, [3] their implementation leads to a change in working methods between the departments involved. Additionally, it requires a precise coordination between the employees, who are becoming co-creators. The innovation process is therefore accompanied by adjustments in the organization. [8]
This leads to a number of challenges.
This leads to a number of challenges.
Challenges
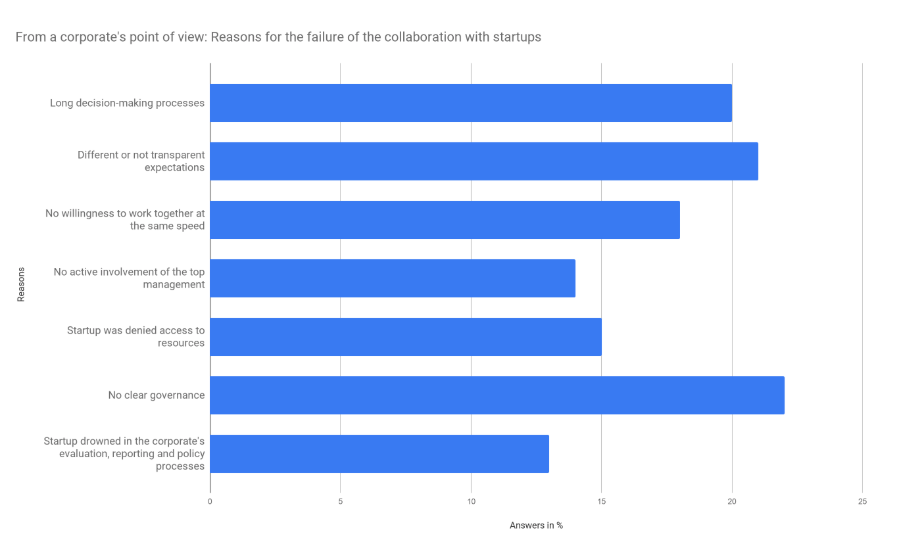
Companies that shrink their accelerator programs or terminate them completely cite stiff processes as a reason. They also complain about too much risk aversion at the cultural level. Finally, the lack of internal resources is mentioned as a reason for poor startup engagement. [7]This leads to delays or the failure of projects in cooperation with startups. [3]
Overall, companies turn out to be too slow. Hierarchically and politically determined decision-making processes often cannot be understood by startups and the impression is created that the partners are not willing to work together at the same speed. [5,3]
In addition, startups often have the feeling that they do not have access to the actual decision-makers of the corporates. As a result, the opinion arises that the wrong cooperation partner has been found. [5]
Even though about 60% of the companies in Germany work together with startups, only ¼ of the startup pilots provide solutions that reach market maturity. [9]
Furthermore, companies often need more than 6 months to close a startup deal, which is a negative factor to success. [9]
This lethargy is mainly due to the numerous manual as well as old-fashioned tasks in data maintenance and reporting, uncoordinated internal and external activities, missing feedback loops as well as duplication of work without the knowledge of the departments involved (silo thinking). [2] Another challenge is that companies do only include few startups in their programs. Since there is not always a fit this can lead to bad results. An issue which is often due to a limited overview of possible startups. [5]
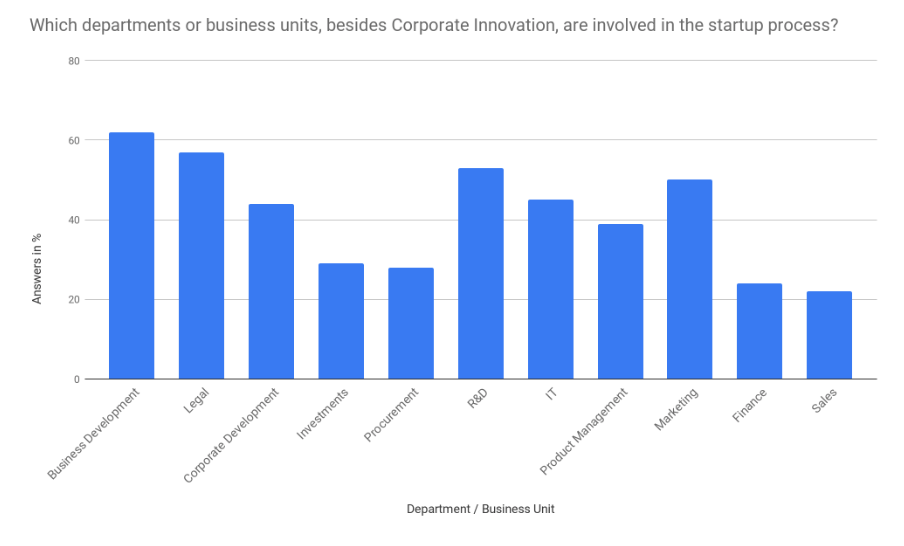
Moreover, the innovation process in large companies often is not clearly allocated. A study of 500 start-ups showed that, in addition to legal and business development, numerous other departments deal with startups. [9]
This lethargy is mainly due to the numerous manual as well as old-fashioned tasks in data maintenance and reporting, uncoordinated internal and external activities, missing feedback loops as well as duplication of work without the knowledge of the departments involved (silo thinking). [2] Another challenge is that companies do only include few startups in their programs. Since there is not always a fit this can lead to bad results. An issue which is often due to a limited overview of possible startups. [5]
Moreover, the innovation process in large companies often is not clearly allocated. A study of 500 start-ups showed that, in addition to legal and business development, numerous other departments deal with startups. [9]
When working with startups, relevant departments such as the legal department, purchasing, etc. are often not involved in time. Resistance also arises because employees are afraid of disruptive external influences. Furthermore, there is a lack of support through the top management. According to 500 startups, there is no clear reporting structure for corporate innovation teams in companies.
Regarding these challenges companies are often hindering themselves. Consequently the company's strategic development department is limited in fulfilling its tasks in order to successfully shape the future. [9]
Advantages Favoring a Strong Corporate Startup Engagement
Through the stronger innovative power of startups, CSEs facilitate the development of products and services and lead faster to innovations.R&D costs can also be reduced. Outsourcing takes place without having to bear the technological risk.
In addition, access is gained to new technologies ("Window on Technology"), talents, know-how and business areas.
Startups act much faster, are digital and focused on niche markets. In fact corporate venture capital units on average register three to four times more patents than R&D departments. [6]
Finally, CSE helps to implement transformation processes. [9]
The cooperation is also worthwhile from a startup’s point of view. Startups gain access to contacts and sales structures. This results in new sales opportunities and financial growth. Ultimately, new references can be identified and, if necessary, an exit option evolves. [3]
Success Factors - How to Implement a Successful Corporate Startup Commitment?
At the beginning it is important to clearly define goals. This refers to which startups are possible opportunities and how to work with them. This includes a clear conception and definition of tasks, the setup and integration of processes - especially the screening process is crucial. A proper integration approach precedes the screening. [4] Moreover, it is of great importance that the defined goals are in line with the corporate goals. This results in a proper corporate startup engagement approach - if, for example, CVS units, accelerator programs or other measures shall be used. [1]Another key success factor is the support through the top management. Here, a certain commitment to innovation has to arise. In addition, the employees' fear of disruptive external developments has to be overcome, which can be achieved by a strong internal communication. The innovative vision and its fit to the corporate strategy has to be made clear. [5] The stakeholders approval can also be gained by small investments in startup relations, e.g. by sponsoring hackathons. Although these are only quick wins, they do convince decision-makers to invest more generously in startup cooperations. [1] Like this, long decision-making processes can be overcome. [9]
For a successful CSE, it is still crucial to build a portfolio of many startups and monitor their performance, by checking relevant KPIs. In order to overcome the lack of transparency caused by the numerous departments involved in the innovation process and their manual working methods in the form of Excel and PowerPoint, it is essential to increase the cooperation between the departments involved. From a corporate’s point of view, cultural differences, often referred to as a major hurdle, can be overcome by reducing risk aversion and giving the start-up insight into technology and customer contacts, in order to reach a value creation. For corporates it is crucial to implement a lean governance for the collaboration with startups, especially in order to counteract the aforementioned differences in processes. [5]
Conclusion
Nowadays companies need to collaborate with startups, in order to succeed in an increasingly competitive market and withstand disruptive developments. M&A activities, accelerator programs and similar measures make it possible to drive innovations quickly and to successfully outsource own R&D efforts.This, however, poses a number of challenges. Companies often act very slowly. There are too many departments integrated into the startup process and they often work in an intransparent way when it comes to reporting and data maintenance. The lack of top management support, risk aversion and cultural differences are additional reasons when collaborations with startups fail.
In order to have a successful corporate startup engagement, a broad portfolio of monitored startups is required. Top management must be involved as well and cumbersome processes have to be overcome by establishing a lean governance. Finally, these steps are only possible if there is a clear definition of objectives, which do fit very well to the company's strategy.
Bibliography
[1] Baurek-Karlic, B. & Brugger, G. (2018). CORPORATE START-UP ENGAGEMENT (CSE): TANGIBLE RETURNS ON INVESTMENT FOR THE MITTELSTAND (SME).[2] BCG The Boston Consulting Group. (2018). The Most Innovative Companies 2018: Innovators Go All In On Digital [Accessed 01 July 2019].
[3] Brigl, M., Gross-Selbeck, S., Dehnert, N., Schmieg, F., Simon, S. (2019). After the Honeymoon Ends: Making Corporate-Startup Relationships Work [Accessed 19 June 2019].
[4] Capgemini (2016). Post-merger integration of small digital companies into larger organizations [Accessed 19 June 2019].
[5] Flötotto, M. (2019). Zusammenspiel von Start-ups und Corporates - Missverständnisse und mögliche Lösungen. McKinsey.
[6] Klamar, N. & Prawet, B. (2018). Corporate Venture Capital Markt in Deutschland. Frankfurt am Main.
[7] Mind the Bridge & Nesta (2019). Open Innovation Outlook [Accessed 19 June 2019].
[8] Riehl, M., Öhler, L., Hessbrüggen, U. (2016). Wohin steuert die Unternehmensentwicklung? Entrepreneure sind die neuen Unternehmensgestalter. [Accessed 01 July 2019].
[9] 500 Startups (2019). Unlocking Innovation Through Startup Engagement: Best Practices from Leading Global Corporations [Accessed 19 June 2019].