Disruptive Innovation – What Are We Actually Talking About?
February 10, 2021
aumentoo’ s End-of-Year Review and Prospects for 2022
January 11, 2022Product life cycles are shortening noticeably. This is especially true for the IT market. Driven by ever new innovations and performance possibilities, today often only three to four months pass before new devices appear on the market. To keep pace with this development, opening up the innovation process is almost inevitable.

But What Exactly Does the Term Open Innovation Mean?
Open Innovation refers to the opening of the innovation process to the outside world in order to increase the innovation potential. Knowledge from customers, universities and suppliers flows into the innovation process. The term Open Innovation was first used by the American economist Henry William Chesbrough. [1]
According to the known economist Joseph Schumpeter, on the other hand, innovations are created within the company and must be developed in a closed form of innovation generation. Therefore, a company develops and markets only its own ideas. Regarding Chesbrough, the emergence of various factors in the dynamic environment at the end of the 20th century challenges the foundations of the closed innovation model. [1]
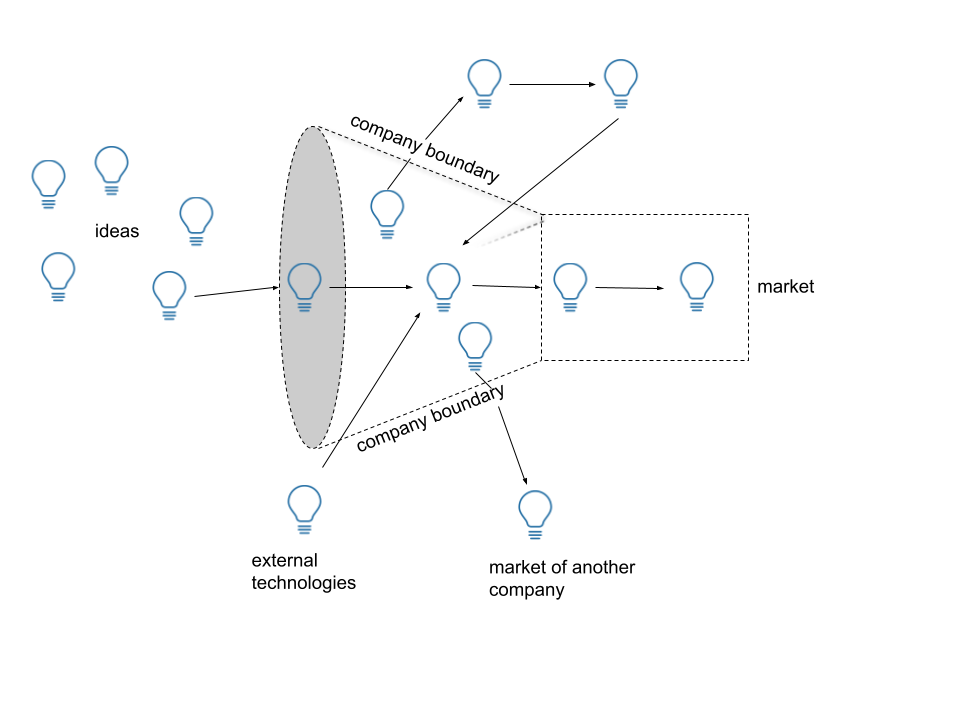
The image describes the opening of a company to innovations from outside. In contrast to closed innovation, Open Innovation involves, for example, an exchange of knowledge between other companies, universities and customers. Ever shorter product life cycles lead to higher pressure to innovate. That's why Open Innovation is becoming even more important today. [1]
Oliver Gassmann and Ellen Enkel describe three different key processes in their paper on Open Innovation [2].
Outside-In vs. Inside-Out vs. Coupled Innovation
Outside-In Process
The outside-in process describes the integration of external knowledge into one's own innovation processes. The knowledge of suppliers, universities and customers should be used to accelerate the progress of the innovation process. By integrating external know-how, the risk of an investment failure can be reduced. For instance, many companies use customer feedback to improve themselves. IBM, for example, has opened up its innovation process to the outside world. For that to happen, IBM holds so-called "Innovation Days", inviting leading scientists, suppliers, customers and potential partners to provide external input on the company's research activities in order to stimulate discussion on common interests and identify emerging business areas at an early stage.Inside-Out Process
The inside-out process describes the externalisation of internal knowledge. Companies use this process to earn royalties on patents or innovations that they do not use for operational business activities. Nokia, for example, has its own patent portfolio because the Research and Development department is so large and many patents are created that Nokia cannot use itself. Currently, Nokia has licensed 200 patents.Coupled Innovation Process
The Coupled Innovation Process aims to develop innovations in alliances, which means combining the outside-in and inside-out processes. For example, HP and Canon have joined forces to develop new printers. Most companies and joint ventures realize that such cooperations cannot work unilaterally. Therefore, care must be taken to strike the right balance between giving and taking. The right partner is crucial for a successful coupled process.Opportunities and Risks of Open Innovation Approaches
Open Innovation brings with it some opportunities and also risks.One risk that can be mentioned is that Open Innovation may lead to an unintentional outflow of internal company knowledge. It can also lead to an increase in the complexity of the innovation process, as many different people work on the same project. Another risk is the internal barriers within the company, for example the negative attitude of employees towards new innovations from outside the company, which can slow down the innovation process. [1]
However, the opportunities of open innovation outweigh the risks.
It helps to increase efficiency in the company. On the one hand, the integration of external knowledge can lead to a considerable shortening of the development times of a product until its market launch. On the other hand, outsourcing innovation activities, for example in the form of scientific cooperation, can contribute to savings in development costs.
Open Innovation leads to a competitive advantage in terms of information over companies that close themselves to innovations from outside. This can be, for instance, cooperation with a start-up or a university. As practical example, Amazon has opted for Open Innovation with the voice assistant Alexa, as its competitor Google's voice assistant continues to grow. In order to keep the information edge, Amazon has launched an annual competition, the Alexa Prize. Teams from different universities are selected to conduct researches under the lead of Amazon scientists and engineers to improve the interaction between humans and AI and create stunning prototypes.
Additional sources of revenue can be generated by sharing internal knowledge. These can be innovations that have nothing to do with the company's business model - as described in the example for the inside-out innovation process.
Furthermore, Open Innovation helps the company to increase its competence. The networking of employees from R&D with colleagues from other departments can prevent operational blindness. [1]
Open Innovation Software to Support the Internal Innovation Process
An Open Innovation Software or Innovation Management Software is a solution to support companies in their innovation process and thus reduce the dangers posed by the aforementioned risks.
What are the Advantages of an Innovation Management Software?

With suitable software, all people involved in the innovation process have insight into the process and can actively contribute, for example through comments, suggestions or evaluations of the innovations/ideas. This not only increases the motivation of each individual but also their commitment. A sense of community among the participants is created and continuously promoted.
People outside the company, such as consultants and service providers, can also be granted access to the data, thereby facilitating their collaboration with the company.
Good software should always be designed in a way that the various user groups have tailored access rights in order to view only the content that is intended for them. This protects sensitive data.

If all information on innovations, project partners, ideas and new technologies is collected, evaluated and analysed in one platform, this increases transparency. Data can be recovered and decisions can be tracked.
Consolidating all information in one tool also prevents certain data from being lost due to the leave of individual employees.
Barriers and resistance to change in the company are best broken down through improved communication and more transparency. These two benefits can be provided by a suitable innovation management software.

The growth in complexity is also seen as a risk of open innovation. However, this can be reduced by using a suitable tool and the innovation process can even be optimised. This is because workflows can be mapped in the software and checked for efficiency.
The use of innovation management software also reduces innovation time, from ideation to product launch in the market. Valuable time can be saved through improved and eased communication between all participants, through the implementation of company-wide process steps, as well as through the automation of manual work. Duplication of work or the parallel work of different departments on similar projects can also be avoided by consolidating the innovation process in one software.
Assessments can be forwarded to experts to help facilitate the decision-making process.
Thus, it can be said that innovation management software leads to better and faster results.
All the points mentioned so far help to establish a culture and a sense of innovation in the company in which the implementation of new ideas and projects is eased and encouraged.
Conclusion
Open Innovation is becoming more and more important in today's world. Due to shorter life cycles of products, the urgency for innovation is increasing. Above all, innovation should be opened for the outside, as this can save considerable costs. With suitable Open Innovation Software, companies are supported in their innovation process and can bring innovations into the company more efficiently. Suitable software helps to unite all participants in one place and to keep them informed about the latest developments. It also helps to establish a sense of innovation in the company.
References
-
[1] A. Braun, E. Eppinger, G. Vladova, S. Adelhelm: Open Innovation in Life Sciences
[2] O.Gassmann, E. Enkel: Open Innovation - Die Öffnung des Innovationsprozesses erhöht das Innovationspotenzial